Archiving vs Backup - Archive Solutions
Archival storage requirements are very different from those of backup operations. Archive systems must offer resilient long-term data storage while meeting the core requirements of supporting legal and mandatory regulatory compliance initiatives.
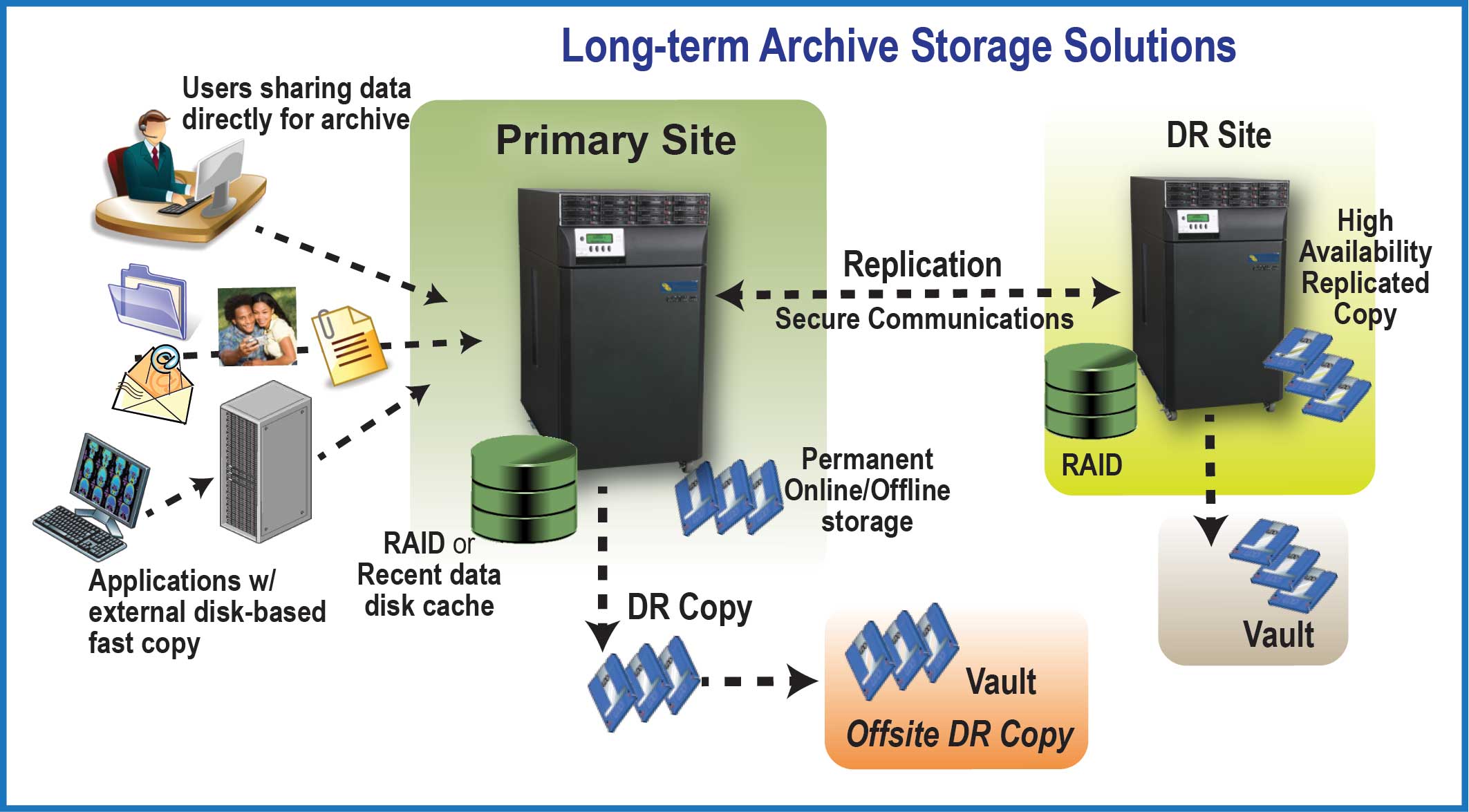
Archive data consists of primary copies of historic data, rather than secondary copies that remain permanent and unalterable. Additionally, media longevity and data authenticity are much more prominent requirements for archive solution environments.
The following illustrates the major functional differences between an archive solution and a backup and recovery Solution. Users or applications will store data on the archive solution that can be thought of as a permanent tier of storage.
Attributes of Archive Solutions include:
- Regulatory Compliance - Provides storage of archive data and associated metadata that meets regulatory guidelines.
- Data Authenticity - In order to comply with corporate and government regulations on data authenticity, it is crucial that information be protected from modification. The storage medium utilized must ensure that data is retained as originally created, guarantee the data’s authenticity, and provide tamper-proof authentication techniques. The associated metadata must be retained along with the data and provided the same levels of protection. Hence, Archive Systems will typically utilize hardware based Write-Once-Read-Many (WORM) storage such as Optical Media to meet these requirements.
- Extended storage medium longevity - Storage medium provides extremely long-term storage life of 50 years or higher, eliminating the need for ongoing data migrations as storage mediums such as tape or HDD deteriorate over time.
- High-performance random read access - For archives, fast random access is typically the most critical performance consideration. Immediate access to random data stored within an archive is essential. Unlike backup solutions, the performance bottleneck for an archive is not read/write streaming, but in providing fast random access to potentially millions of records requested by thousands of users
- Low long-term total cost of ownership - Archive solutions are much more cost effective for managing static data as they eliminate costs related to data backup, power, cooling, and ongoing storage management overhead such as data migrations.
Though disk-based storage (RAID) is an important component of an archive solution, which will provide caching of frequently accessed fixed content data, it does not replace the capabilities of a resilient storage medium such as optical media storage. RAID, while offering unmatched performance and high capacity, is fundamentally a rewritable media with a life span of several years. It cannot be taken off-line for secure vaulting, and the long-term operating cost for RAID storage is costly. By contrast, optical is removable, has high capacity, provides for long-term preservation of data, and offers fast random read/write access capabilities.
