Selecting the Right Technology
Behind every data archiving system there is technology (hardware and accompanying software) that actually stores the data, even if it is in the cloud. There are many factors involved with determining the right technology on which to store data including costs, maintenance, special environmental conditions (cooling/humidity), frequency of access, and the duration of retention.
Generally speaking, there are really three core technologies used for storing data:
- Magnetic Spinning Disk Systems: Magnetic spinning disks provide excellent performance and capacity but the only way to protect against inadvertent data loss is to implement some form of short-term data backup or replication to recover the lost data.
- Tape Based Systems: Tape technology also provides high capacity, but actually compounds the risk of data loss if a single tape is damaged. Tape is a fragile media that wears with use and can become unstable due to environmental conditions.
- Optical Based Systems: Optical technology provides the most stable of the three storage technologies as it is a non- magnetic, non-contact media. Once data is written on optical media, such as Plasmon UDO™ media or Blu-Ray™ media, there is little risk of data loss in normal operating conditions, eliminating the need for short-term backup. Unlike tape, UDO and Blu-Ray™ media have a very high tolerance to environmental conditions and typically require no on-going maintenance.
Each of these technologies has a value position in the storage operation and can all be combined and used together in a storage environment based upon data storage management design. The combination of these technologies, appropriately applied to the data storage operation, is referred to as a Tiered Storage Strategy.
One major consideration in deciding which technology is best for each tier is to determine 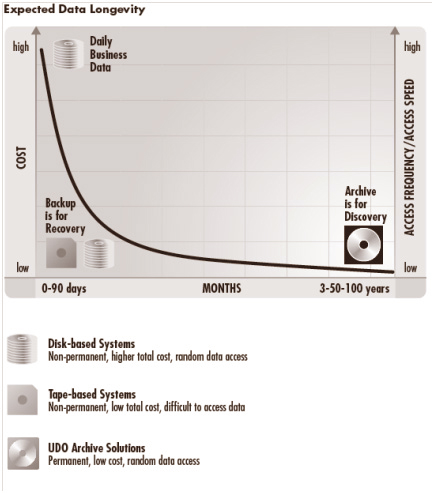
how long data needs to be retained.
- 4 to 5 years - Magnetic Disk Systems
- 3 to 9 years - Tape based systems
- 3 to 50 + years - Optical based systems
The Tiered Storage Strategy
Disk arrays, tape and optical archive solutions all have a place in a Tiered Storage Strategy.
Highly redundant disk arrays, at the highest price point, should be used for normal business operations (in other words, active or production data) with high-access, high-availability, and short-term data storage requirements.
Tape and disk based solutions are excellent for backup and recovery strategies and provide quick capture of data in order to restore data on the disk arrays in the event of a disaster or other loss. The data backups are saved for a short period with tape backup media being recycled.
Optical media is the solution for permanent archiving in circumstances where data must be preserved unaltered, retained for extended periods, and randomly accessed. Because it is fixed-content data and infrequently accessed, it can be removed from expensive primary disk arrays onto optical media reducing costs and backup-window time frames.
Any organization required to keep data for extended periods (due to HIPAA, Sarbanes-Oxley, or other regulatory compliance) will benefit from a tiered storage strategy that addresses active data, data backup and recovery and archival data requirements.
By creating storage tiers according to business use of the data, data longevity, management requirements, and discovery needs, customers will see improved operational and management efficiencies with shortened backup windows and reduced costs. The costs of primary storage are reduced as data is off-loaded to archive systems.
